District-specific Literacy Rates, 2001: Preliminary Analysis
Census of India 2001: Preliminary Analysis of District-specific Literates and Literacy Rates, 2001
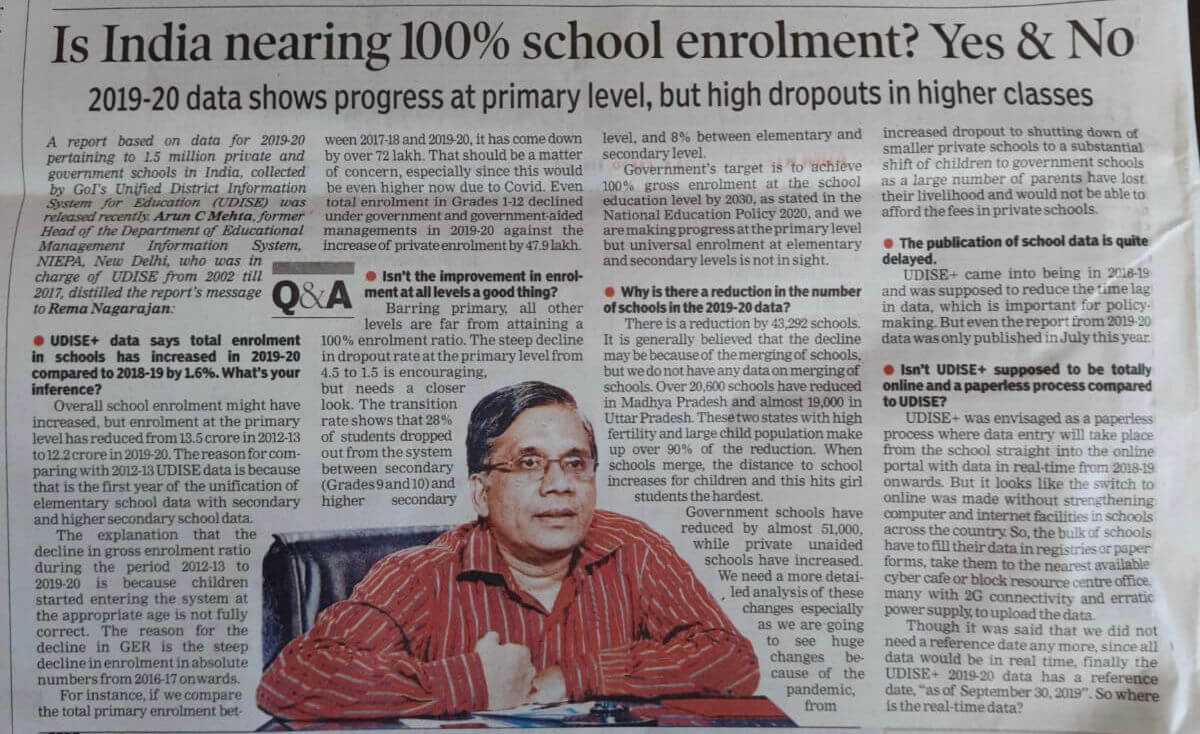
ARUN C MEHTA
NIEPA, 17-B, Sri Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi – 110017 (INDIA)
- Dantewada district (30.01%) of Chattisgarh has the lowest literacy rate while Aizawl district (96.6%) of Mizoram has the highest literacy rate in 2001
- About 81 districts have literacy rate lower than 50 per cent
- About 297 districts have lower literacy rates than the national average of 65.38 per cent
- 23 districts in Bihar, 8 in Jharkhand, 7 in Orissa, 18 in Uttar Pradesh etc. have lower than 50 per cent literacy rates
- More than 59 districts have above 80 per cent literacy rates, most of the districts of Kerala and Mizoram have above 80 per cent literacy rates
- 23 of the 37 districts of Bihar have below 50 per cent literacy rates
- Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh together have 57 districts that have lower than 50 per cent literacy rate of the total 81 such districts
- Kishanganj (18.49%) district of Bihar has the lowest female literacy rate while Aizawl (96.06%) district of Mizoram has the highest female literacy rate in the country
- Both the male and female literacy rates in Aizawl district of Mizoram are the highest in the country
- In about 253 districts, the female literacy rates are lower than 50 per cent
- 313 districts have lower female literacy rates than the national average of 54.16 per cent
- Some of the states which have a number of districts below 50 per cent female literacy rates are: Andhra Pradesh (14), Arunachal (10), Bihar (36), Gujarat (7), J & K (11), Jharkhand (15), Karnataka (7), Madhya Pradesh (24), Rajasthan (25), Orissa (15), Uttar Pradesh (53)
- While in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan, only 3 districts have lower than 50 per cent literacy (Total) rate but the same in case of female literacy rate is 24 (Madhya Pradesh) and 25 (Rajasthan) districts
- Dantewada district (39.59%) of Chattisgarh has the lowest male literacy rate and Mahe district of Pondicherry, the highest male literacy rate (97.59%)
- Only 20 districts have male literacy rates lower than 50 per cent
- 32 districts have more than 90 per cent male literacy rate and 227 districts above 80 per cent
- 323 districts have male literacy rates above the national average of 75.84 per cent
- Jaintia hills districts of Meghalaya is the only district in the country which has higher female literacy rate (55.54%) than male literacy rate (50.52%)
- In about 11 districts, male/female differential in literacy rate is lower than 5 percentage points, most of which are the districts from Kerala and Mizoram
- The highest male/female differential in literacy rate is noticed in Sawai Madhopur district (41.31%) of Rajasthan
- In about 100 districts, the male/female differential in literacy rate is above 30 percentage points as against 222 districts having more than 25 percentage points differential
- 310 districts have higher differential in male/female literacy rate than at the national level (22%)
- 546 of the total 593 districts of the country have male/female differential above 10 percentage points
- Murshidabad district of West Bengal has the highest number of illiterates (21.74 lakh, 7 & above) population
- Mahe district of Pondicherry has the lowest number of illiterates, it has only 363 male and 1025 female illiterates
- 67 districts have more than 10 lakh illiterates of 7 and above population
- Bihar, Chattisgarh, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Uttaranchal together have 202 of the total 593 districts of the country. These states together have more than 129 million illiterates of the total 301 million illiterates in the country